Marketing & Market Types
Marketing is a study of markets. Market needs an exchange.
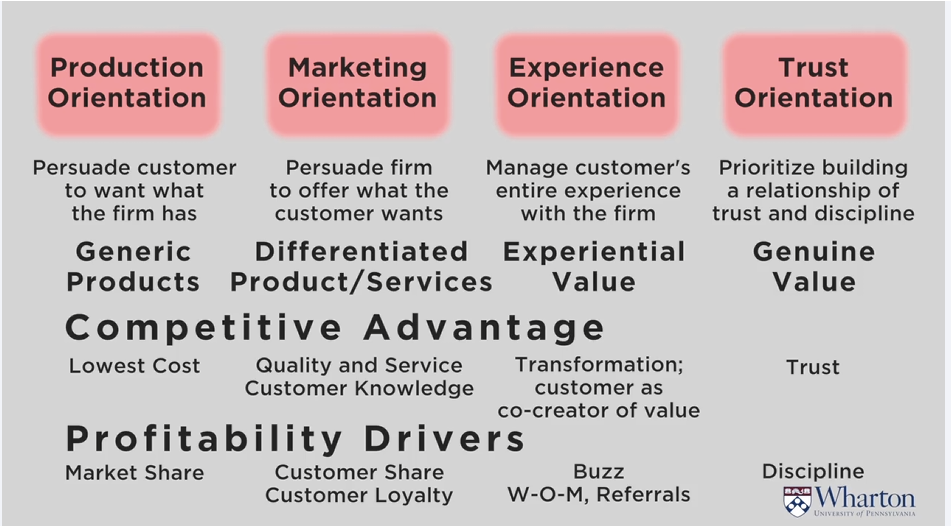
Sellers' market:
- Seller has the market and has all the power. Buyers come to you.
- Focus on the company, product.
- Sell as much as you can.
- Profitability comes from volume.
- Market share becomes a business objective.
Buyer's market:
- Buyer has the power, there are many producers competing for a buyer's attention.
- Marketing: focus on the customer and competition.
- Look what customer wants and deliver what they want.
- You can't focus on every customer.
- Segment your customers.
- Profitably comes from coming value to the customer, where customers want the premium for.
- Customer share becomes a business objective.
- Develop customer loyalty
Cross-selling is selling other things beside one specific product. E.g., when buying jeans, sell a belt next to it.
In today's connected world, it is important not only to deliver value to the customer but also the best user experience. Especially, in a buyer's market, where developing customer loyalty is important.
User experience is a user journey that includes also experiences before and after transaction.
Customer trust: offer authentic genuine customer value.
Discipline - reduced costs.
3 principles of Marketing:
- Principle of Customer Value. Offer real genuine customer value.
- Principle of Differentiation. You have to provide value better than the competition.
- Principle of Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning. You can't deliver value to all. Choose your customer and deliver what's best for them.
4 P's of Marketing:
- Product. What the seller puts into an exchange.
- Place. Method of distribution, e.g. physical store, online store.
- Promotion. The way the seller communicates the benefits of the product, e.g. advertising.
- Price. What the buyer puts into an exchange.
No comments to display
No comments to display